WiFi 6 Speed Explained: Boosting Your Home Network

A lightning-fast internet speed is necessary in the age of high-definition streaming, online gaming, and remote work. WiFi 6, the latest wireless technology, has come into play. In theory, the maximum speed of WiFi 6 can go up to 9.6 gigabits per second. This article will unveil the maximum speed of WiFi 6, key factors affecting the WiFi 6 speed, and how to optimize the WiFi 6 speed for your home network.
What is the Max. WiFi 6 Speed?
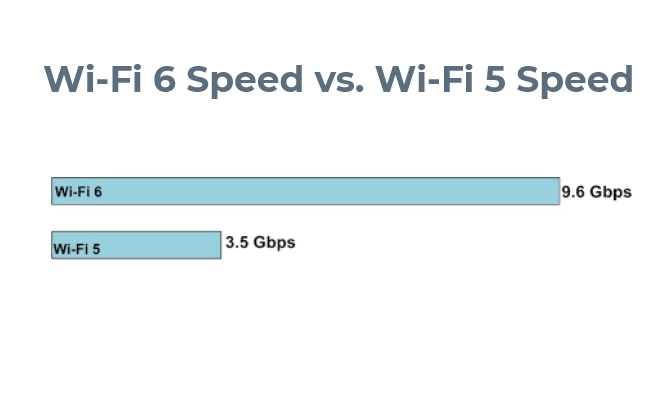
WiFi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is the latest improvement in wireless technology that offers substantially faster speeds than its predecessor. Theoretically, the max WiFi 6 speed can reach 9.6 Gbps (gigabits per second).
In practical, everyday usage, WiFi 6 speeds are typically much lower than the maximum theoretical speeds. For example, in typical home and office environments, the WiFi 6 speed limit can range from about 600 megabits per second (Mbps) to about 4.8 or more gigabits per second (Gbps) under optimal conditions. The exact speeds will vary from one setup to another.
What Makes WiFi 6 Speed Faster?
WiFi 6 speed is faster than its predecessors primarily due to various technologies and improvements.
Wider Channel Bandwidth
WiFi 6 introduces higher maximum data rates, and it achieves this by utilizing wider channel bandwidths, such as 160 MHz channels, which can transmit more data in a given time frame.
The channel bandwidth refers to the amount of radio spectrum that a wireless signal can use to transmit data. In WiFi networks, the channel bandwidth determines how much data can be transmitted in a given period and impacts the overall WiFi 6 speed.
In WiFi technologies, common channel bandwidths include 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, and 160 MHz. The wider the channel bandwidth, the more data can be transmitted simultaneously. For instance, 160 MHz channels in WiFi 6 can provide significantly higher speeds than 20 MHz channels.
OFDMA
WiFi 6 uses OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) to improve efficiency and performance. OFDMA divides the frequency spectrum into smaller sub-channels, each of which can be allocated to different devices or users. This division allows multiple devices to transmit data simultaneously within the same frequency band, significantly reducing contention and interference. As a result, more devices can share the spectrum efficiently, leading to higher overall speeds of WiFi 6.
MU-MIMO
WiFi 6 supports MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output), contributing to its speed. MU-MIMO allows the router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously, and different antennas serve each device independently. It also enables the router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously, both in the downlink and uplink directions. With MU-MIMO, WiFi 6 can transfer data much faster and reduce latency.
Improved Modulation Schemes
The modulation scheme is another fundamental aspect of WiFi technology and plays a vital role in determining the speed and efficiency of the WiFi connection. Modulation refers to how digital data is converted into analog signals for transmission over the wireless medium. Different modulation schemes have distinct complexity levels, allowing for varying data rates and reliability. Generally speaking, modulation schemes directly affect WiFi speed by determining how much data can be transmitted in a given period.
In the context of WiFi 6, the modulation scheme is 1024-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), which represents 1024 different amplitude and phase combinations to encode digital data for transmission. Using 1024-QAM allows for higher data rates in wireless communication systems, as more information can be encoded and transmitted in a given period, making 1024-QAM particularly useful in improving WiFi 6 speed.
WiFi 6 Speed vs. WiFi 5 Speed: Which One is Faster?
There are several differences between WiFi 5 and WiFi 6. Undoubtedly, WiFi 6 speed is much faster than WiFi 5 speed. WiFi 5 offers maximum theoretical data rates of up to 3.5 Gbps (gigabits per second), while WiFi 6 offers top theoretical data rates of up to 9.6 Gbps. The speed of these two wireless technologies can differ in the following aspects:
- Real-World Speed: In practical real-world scenarios, WiFi 5 typically provides speeds ranging from 300 Mbps to 1.7 Gbps. On the other hand, WiFi 6 can provide speeds ranging from 600 Mbps to 4.8 Gbps or more in real-world usage.
- Modulation Schemes: WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 also use different modulation schemes. WiFi 5 uses lower-order modulation schemes like 256-QAM, representing up to 8 bits per symbol. WiFi 6 introduces higher-order modulation schemes, including 1024-QAM, representing up to 10 bits per symbol. The higher-order modulation schemes allow for more efficient data transmission.
- Wireless Technologies: The efficiency of wireless technologies used in WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 also affects the speed. The MU-MIMO technology in WiFi 5 can handle multiple devices but is less efficient and slower than WiFi 6's MU-MIMO. WiFi 6 also employs advanced technologies like OFDMA, while WiFi 5 only uses OFDM.
WiFi 6 Speed Test: Result & How to Perform
A noticeable disparity exists between the theoretical speed of WiFi 6 and real-world performance. Performing a WiFi 6 speed test can empower users to optimize their connectivity.
Understanding WiFi 6 Speed Test Results
Before performing the test, testers must understand the various metrics used to evaluate the speed. Some essential factors may be included in the WiFi 6 speed test results.
- Download Speed: This is the speed at which data is received from the internet to your device. It's an essential metric for streaming, downloading files, or browsing the web. Higher download speeds mean faster content delivery. It is typically expressed in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
- Upload Speed: This is the speed at which data is sent from your device to the internet. It's crucial for video conferencing, uploading files, or online gaming. It is typically expressed in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
- Latency (Ping): Latency, often measured in milliseconds (ms), represents the time it takes for data to travel from your device to a server on the internet and back. Lower latency values indicate a more responsive connection, essential for online gaming and video conferencing.
- Jitter: It is the variation in latency over time. A consistent, low jitter is desirable, as it ensures smooth and predictable data delivery. High jitter can result in stuttering or lag during activities like VoIP calls or online gaming.
- Packet Loss: Packet loss occurs when data packets don't reach their intended destination. Even a small amount of packet loss can disrupt real-time applications. A low or zero percent packet loss is preferred.
How to Perform WiFi 6 Speed Test
Many tech lovers are curious about the real-world speed of WiFi 6 in different usages and choose to perform the speed test at home. Here are some general steps to follow if you are one of them.
- Prepare Your WiFi 6 Setup: Your WiFi router or access point needs to be WiFi 6-compatible. On the other hand, the connected devices, such as laptops or smartphones, also need to support WiFi 6.
- Choose a Speed Test Service: You must use a third-party test service or app to test the speed. Online speed test services, such as Ookla's Speedtest.net, Fast.com, and Google's Speed Test, are available. You can use a web browser to access these services or download their apps from app stores.
- Connect to Your WiFi 6 Network: Before starting the test, connect your device to the WiFi 6 network. You can do this by selecting your WiFi 6 network from the list of available networks and entering the appropriate credentials.
- Run the Speed Test: Open your device's chosen speed test service (website or app). Click the "Begin Test" or "Go" button to initiate the test.
- Wait for Results: The speed test will measure your download and upload speeds, latency (ping), and possibly other metrics like jitter and packet loss. These results will be displayed on your screen once the test is complete.
- Analyze and Repeat the Results: Examine the test results, focusing on the above key metrics. For a more accurate assessment, consider running the test multiple times at different times of the day. This can help you evaluate your WiFi 6 network's performance consistency.
How to Optimize WiFi 6 Speed at Home
If you get unwanted WiFi 6 speed test results, you must take measures to level up your WiFi 6 speed.
Use WiFi 6-Compatible Devices
WiFi 6 requires its unique compatible devices. Ensure that your router or access point and the devices you connect to the network are WiFi 6-compatible. You can check the product specifications or ask the seller for detailed information.
Choose the Right WiFi 6 Router
Your WiFi router must support WiFi 6. Many routers in the market now are WiFi 6-compatible. You can select a high-quality WiFi 6 router with advanced features, such as MU-MIMO, OFDMA, and beamforming, to maximize network speed.
Optimize Router Placement
Choose a better WiFi router placement. In a household or office, you can place the router in a central location and elevate it to a certain height. Protect the router from obstructions like walls, furniture, and metal objects. An optimized placement can enhance the signal coverage and quality.
Use the Appropriate Channel Width
WiFi 6 routers support different channel widths (e.g., 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, 160 MHz). Choose the appropriate channel width based on your needs and interference levels. Wider channels can provide higher speeds but may be susceptible to more interference.
Enable QoS and WP3
If multiple devices and applications share the same WiFi 6 network, remember to enable QoS and WP3. QoS is a set of technologies used to manage and prioritize network traffic. For example, QoS allows network administrators to assign different priority levels to various types of network traffic. For example, real-time applications like VoIP (Voice over IP) or video conferencing can be prioritized over non-time-sensitive tasks like file downloads.
WP3 is an advanced security encryption that WiFi 6 uses. It provides a more robust layer before your WiFi 6 network and can seamlessly protect the network from potential threats and interferences.
WiFi 6 Speed vs. WiFi 6E Speed: What's the Difference?
WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E are related wireless technologies with the same theoretical speed, up to 9.6 Gbps. However, they differ primarily in frequency bands and available spectrum, directly impacting their speed and performance.
WiFi 6 (802.11ax) operates in the 2.4 GHz, and 5 GHz frequency bands, but WiFi 6E has access to the 6 GHz band in addition to the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, which enables it to provide similar maximum theoretical speeds as WiFi 6 but with improved real-world performance due to reduced interference and congestion. WiFi 6E is particularly suitable for applications that demand high-speed, low-latency, and interference-free wireless connections, such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and ultra-high-definition video streaming.
FAQs
What is the max speed of WiFi 6?
The maximum theoretical speed of WiFi 6 (802.11ax) is up to 9.6 Gbps (gigabits per second). In everyday situations, WiFi 5 commonly delivers speeds between 300 Mbps and 1.7 Gbps, while WiFi 6 can often offer speeds ranging from 600 Mbps to 4.8 Gbps or even more.
Is WiFi 6 speed faster than WiFi 5 in the real world?
The answer is yes. WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 differ significantly in theoretical speeds. In real-world applications, the speed of WiFi 6 is much faster than that of WiFi 5, with typical speeds ranging from 600 Mbps to 4.8 Gbps or even more.
Can I perform a WiFi 6 speed test at home?
Of course you can! Testing WiFi 6 speed at home allows you to assess the performance of your network and make any necessary improvements. But you must have WiFi 6-compatible devices and ensure your router supports WiFi 6. Before testing, choose an online speed test service or download a speed test app to deliver the results.
Conclusion
WiFi 6, with its advanced features like OFDMA, MU-MIMO, and 1024-QAM, brings significant improvements in terms of speed over its predecessor, WiFi 5. To enhance network performance at home, users can conduct WiFi 6 speed tests to gauge their network's real-world performance accurately. At the same time, with the emergency of WiFi 6E and its access to the 6 GHz band, users can anticipate even more remarkable speeds and reduced interference.
Did you upgrade your home network to WiFi 6? What's your idea about the WiFi 6 speed? Please share your thoughts with us, and let's discuss them together in the comment section below!
Search
Subscribe for the Latest Updates
Security insights & offers right into your inbox