What's the Difference between Cat6 and Cat6a?
In the network, the type of Ethernet cable you choose can make a substantial difference in your connection quality and data transmission speeds. Cat 6 (Category 6) and Cat 6a (Category 6a) cables are two stalwarts in the networking cables, each with its own strengths and capabilities. Before establishing or upgrading your network infrastructure, it's crucial to understand the distinctions between these two cable options.
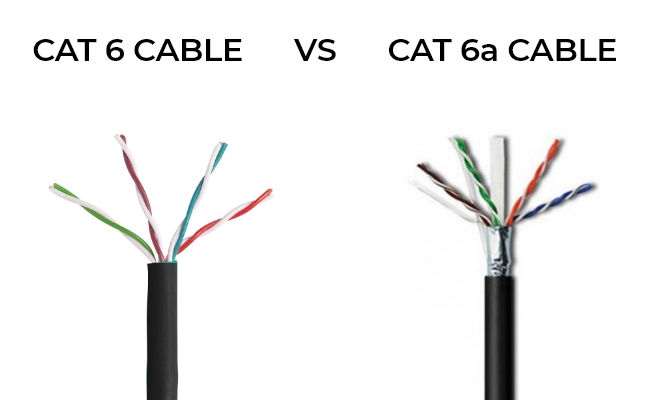
Cat6 vs. Cat6a Ethernet Cables: Key Differences
The biggest difference between cat6 and cat6a ethernet cables lies in their data transfer speed. Cat6a ethernet cable speed is at least 500 MHz and allows 10 Gbp/s data transmission up to 328 feet (100 meters), while cat6 cable max speed is only 250 MHz and only supports 10 Gbp/s to 165 feet (55 meters) with reduced crosstalk. Apart from this, they also differ from each other in the following aspects:
Speed and bandwidth
Cat 6 cables support data transfer max speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps) over a maximum distance of 100 meters (approximately 328 feet). They have a bandwidth of 250 MHz. While, Cat 6a cables are designed to handle data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps over a longer distance, up to 100 meters (approximately 328 feet). They have a significantly higher bandwidth of 500 MHz.
Shielding
Cat 6 cables commonly feature U/FTP (Unshielded with Foil Twisted Pair) or F/UTP (Foiled Twisted Pair) configurations, which provide a layer of overall foil shielding. Some Cat 6 cables may not have individual pair shielding, relying primarily on the foil shielding for EMI protection.
Cat 6a cables often incorporate more robust shielding options, such as S/FTP (Shielded with Foil Twisted Pair) or F/FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair) configurations. In addition to the overall foil shield, Cat 6a cables usually have individual pair shielding, offering enhanced protection against electromagnetic interference and crosstalk.
Cable thickness
Cat 6 cables are typically thinner and more flexible than Cat 6a cables, which can make them easier to work with in tight spaces or when bending around corners.
Cost
Due to their high-quality materials, Cat6a cables come at a higher cost than Cat6 cables. Moreover, upgrading a network to Cat6a entails cable replacement and adopting higher-performance switches and other network infrastructure components.
Patch panels for servers
In practical terms, there are no significant distinctions between Cat6 and Cat6a patch panels. However, it's important to note that the larger dimensions of Cat6a cables and their resulting increased minimum bend radius can alter the installation demands, cable handling procedures, and considerations for pathway and space design.
Comparison table
Here is a comparison table of cat 6 and cat 6a:
Cat 6 vs cat 6a: Basic of Them
After knowing the key differences of cat 6 and cat 6a, let's explore their details.
What is cat 6?
Cat 6 is a standardized twisted-pair Ethernet cable that employs the familiar 8P8C connector, also known as RJ45, on both ends. This design ensures backward compatibility with earlier Ethernet cable standards like Cat 5e, Cat 5, and their predecessors.
Despite this compatibility, Cat 6 stands out for its elevated performance capabilities, accommodating speeds of up to 10 Gbps across distances spanning up to 55 meters. It's noteworthy that beyond this 55-meter length and up to the standard Ethernet maximum of 100 meters, the data rate aligns with Cat 5e, capping at 1 Gbps.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness and widespread availability of Cat 6 cables contribute to their prominence as a favored choice for networks in residential settings and small to medium-sized businesses.
What is cat 6a?
Cat 6a cables build upon the advantages of Category 6 cables while elevating their capabilities through enhanced performance and superior shielding. These cables can support higher frequencies, rendering them adept at handling elevated data rates across extended distances. With a rating of 10 Gbps over 100 meters, Cat 6a cables excel in delivering improved performance due to upgraded shielding and decreased crosstalk among the cable's twisted pairs.
Cat 6a cables prove particularly advantageous in scenarios demanding dependable, high-speed connectivity. These encompass applications like data centers, enterprise networks, and settings where the imperative is to curtail interference and signal attenuation.
Types of Cat6 and Cat 6a cables
Broadly speaking, Cat6 and Cat6a cables can be classified into two main categories: shielded and unshielded. Shielded cables typically incorporate an outer shielding layer around individual twisted pairs or all pairs collectively. Depending on the intended usage, varying degrees of shielding are available to cater to diverse applications.
-
U/UTP: Commonly known as UTP, this is the prevailing and widely embraced cable type. Comprising four twisted pairs, UTP lacks a shielding structure. Despite this, it features symmetrical pairs and a balanced design that aids in mitigating NEXT (Near-End Crosstalk).
-
F/UTP: F/UTP indicates a cable with four unshielded twisted pairs enveloped by an overarching outer foil shield. This shielding mechanism provides a degree of protection against interference.
-
U/FTP: U/FTP does not boast external shielding, but each twisted pair possesses an individual foil screen. This arrangement serves to deter crosstalk interference.
-
F/FTP: F/FTP incorporates four foil-shielded twisted pairs, fortified by an external foil shield. This design enhances the shielding for improved signal integrity.
-
S/FTP: S/FTP combines the shielding prowess of four foil-shielded twisted pairs with an overall outer braid screen. This robust shielding structure bolsters protection against external interference.
-
SF/FTP: Offering the utmost safeguarding against interference, SF/FTP boasts a dual-layer defense. It features both braid and foil shielding in conjunction with foiled twisted pairs, ensuring comprehensive protection for the cable.
Cat 6 vs. Cat 6a: Which Cable Should You Choose?
Let's explore some scenarios in which you might choose either Cat 6 or Cat 6a Ethernet cables based on specific networking needs.
Home network with standard usage
If you're setting up a basic home network for everyday internet browsing, streaming, and occasional online gaming, Cat 6 cables are likely sufficient. They offer 1 Gbps speeds, which are more than enough for standard household activities. Cat 6 cables are also thinner and more flexible, making them easier to install around your home.
Large office or data center
In environments where a significant amount of data needs to be transmitted quickly and without interruption, Cat 6a is preferable. Cat 6a's 10 Gbps speeds and enhanced shielding help prevent crosstalk and interference, making it suitable for data centers, larger offices, and professional settings.
Future-Proofing for network upgrades
If you're planning for future network upgrades or want to ensure your cabling infrastructure remains relevant for years, Cat 6a is the better choice. It supports higher bandwidth, making it more suitable for handling new technologies and increased data demands.
The Similarity of Cat 6 and Cat 6a
While Cat 6 and Cat 6a possess distinct features that set them apart, notable similarities form the common ground upon which their capabilities are built.
RJ45 connectors
An RJ45 connector, also known as an 8P8C connector, is the universal interface for Ethernet cables. Both Cat 6 and Cat 6A cables utilize this familiar connector type, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of networking devices and equipment.
Maximum data rate
Both cable types share the same maximum data rate of 10 Gbps (gigabits per second). This means that whether you opt for Cat 6 or Cat 6A, you're assured of their capability to handle high-speed data transfer, making them suitable for various applications.
Backward compatibility
Both Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables are designed with backward compatibility in mind. They can be seamlessly integrated into existing networks that use earlier Ethernet standards, such as Cat 5 and Cat 5e. This feature ensures a smooth transition when upgrading network components.
Twisted pair design
Both Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables are built upon the foundation of a twisted pair design. This entails four pairs of copper wires, each individually insulated and twisted together. This design minimizes electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, improving signal integrity and data transmission quality.
Cat5 vs. Cat 6 vs. Cat 6a vs. Cat 7: What's the Difference?
Besides Cat 6 and Cat 6a, someone may be interested in Cat 5 and Cat 7. Let's explore their distinctions.
What is Cat5?
Cat 5 is typically the baseline standard for hosting VoIP services. The numeric designation signifies the cable's data-handling capabilities, with Cat 5 supporting a maximum speed of 10/100 Mbps and a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz.
What is Cat7?
Cat 7 Ethernet cables are distinct within the Ethernet cable landscape. Notably, they are not recognized by industry-standard organizations such as TIA or the EIA.
Despite this, Cat 7 cables offer remarkable capabilities, surpassing Cat 6A in terms of bandwidth with an impressive 600MHz capacity. They also introduced support for 10Gbps Ethernet speeds several years ahead of Cat 6A's approval.
However, what sets them apart is their utilization of TERA GG45 connectors instead of the more common 8P8C connectors. While Cat 7 cables can still work with 8P8C connectors, this unconventional choice in connectors made them less suitable for standard network installations.
Comparison between Cat5 vs. Cat 6 vs. Cat6a vs. Cat7
FAQs
1. Is Cat6A better than Cat6?
If you're building a new network or upgrading an existing one and anticipate the need for higher speeds and longer cable runs, Cat6a is a worthwhile investment. However, if Cat6 can meet your current requirements and cost is a significant concern, Cat6 may still be a viable option. Ultimately, the decision should be based on your specific networking needs and budget.
2. What are the disadvantages of Cat6a cable?
One drawback is its cost. Cat6a cables are generally more expensive than Cat6 cables due to their thicker and more intricate design. This can make them less cost-effective for smaller-scale installations or budgets prioritizing cost savings.
Another disadvantage is their increased bulkiness. Cat6a cables are thicker and less flexible than Cat6 cables, which can make them more challenging to install in tight spaces or through conduits.
3. Is Cat6 compatible with Cat6A?
Yes, Cat6 and Cat6A are compatible and use the same RJ45 connectors. The connection will run at the lower standard’s speed, so full Cat6A performance requires Cat6A cables and ports end to end.
4. Is it worth upgrading from Cat5e to Cat6a?
Upgrading from Cat5e to Cat6a can be a worthwhile investment if you require higher bandwidth, plan for future-proofing your network, need to cover longer cable distances, or operate in environments with potential interference issues.
Cat6a provides significantly better performance, supports faster data transfer rates, and offers improved resistance to crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. If your network demands 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GbE) or higher speeds, Cat6a is a suitable choice.
Conclusion
Whether you choose Cat 6 vs Cat 6a, it's essential to ensure proper installation and maintenance to maximize their performance. Investing in quality cables, connectors, and professional installation will help you make the most of your network infrastructure, regardless of the category you select.
If you like this article and find it helpful, share it with your friends. Got something to say about ethernet cables? Make sure you leave a comment below!
Search
Subscribe for the Latest Updates
Security insights & offers right into your inbox