Night Vision vs. Infrared: What's the Difference?
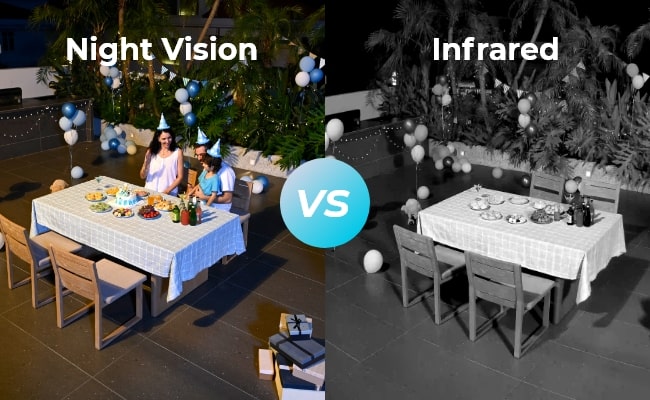
In the world of visual technology, two terms that often come up are "night vision" and "infrared." While these technologies, night vision vs infrared, may seem similar, they have distinct differences that are important to understand. In this article, we will look into the fundamental differences between infrared vs night vision, exploring their working principles, image quality, and applications.
- Infrared vs. Night Vision: Understanding the Basics
- Night Vision vs. Infrared: Key Differences
- Night Vision vs. Thermal vs Infrared: Comparison Table
- Infrared Binoculars vs. Night Vision: Pros and Cons
- Color Night Vision vs. Infrared: Which is Better for Security Cameras?
- Best Security Camera with Night Vision Recommendation
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Infrared vs. Night Vision: Understanding the Basics
First, let’s understand what is the basic definition of infrared and night vision:
What is Night Vision?
Night vision refers to the ability to see in low light or even complete darkness. This technology works by amplifying the available light, including infrared light, which is invisible to the human eye. Night vision devices, such as goggles and cameras, use specialized sensors to detect and amplify these faint light signals, creating an enhanced image that allows users to see clearly in the dark.
What is Infrared?
Infrared (IR) is a type of electromagnetic radiation that has a longer wavelength than visible light. Unlike visible light, infrared radiation is not detectable by the human eye. Infrared technology, on the other hand, utilizes this invisible radiation to detect and measure heat signatures, or thermal energy, emitted by objects. Infrared cameras and sensors can create images based on the differences in temperature across a scene, allowing users to see in the dark and even detect hidden objects.
Night Vision vs. Infrared: Key Differences
The most significant difference between night vision and infrared is the source of the image they provide: night vision technology utilizes either visible or infrared light to generate images, whereas infrared devices produce images by detecting thermal energy.
Source of Image
Night vision devices rely on amplifying available light, including visible light and infrared light, to create an enhanced image. They essentially "see" the same thing that the human eye would see, just with a higher level of sensitivity.
Infrared, on the other hand, detects and measures thermal energy, or heat signatures, emitted by objects. This means that infrared systems can "see" in complete darkness, as they are not dependent on ambient light levels.
Working Principle
Night vision technology works by using a photocathode to convert the available light, including infrared, into an electrical signal. This signal is then amplified and converted back into a visible image.
Infrared technology, in contrast, uses specialized sensors to detect the infrared radiation emitted by objects. The sensors measure the differences in temperature across a scene and translate that information into a visual representation.
Image Quality
Night vision images tend to have a higher resolution and more natural color representation compared to infrared. This is because night vision devices are amplifying the available light, which includes the full spectrum of visible light.
Infrared images, on the other hand, are often presented in grayscale or false color, as they are not capturing the visible light spectrum. The image quality can also be affected by factors such as atmospheric conditions and the sensitivity of the infrared sensors.
Technology
Night vision technology relies on image intensifier tubes or electronic image sensors to amplify and convert the available light into a visible image.
Infrared technology, in contrast, uses specialized thermal sensors, such as microbolometers, to detect and measure the infrared radiation emitted by objects.
Types
Night vision devices can be categorized into different generations, with each generation offering improved performance and capabilities.
Infrared technology can be further divided into two main types: thermal imaging and active infrared. Thermal imaging uses passive infrared sensors to detect heat signatures, while active infrared uses a source of infrared light to illuminate the scene.
Night Vision vs. Thermal vs Infrared: Comparison Table
To further illustrate the differences between night vision vs infrared vs thermal, we will compare them in a table. Let’s take a look at the comparison between infrared vs thermal vs night vision:
Infrared Binoculars vs. Night Vision: Pros and Cons
Here, we also indicate the pros and cons of each technology.
Infrared: Advantages and Downsides
The following are the advantages and downsides of Infrared binoculars:
Advantages:
- Ability to detect heat signatures in complete darkness
- Can see through smoke, fog, and other atmospheric conditions
- Useful for security and surveillance applications
Downsides:
- Lower image quality compared to night vision
- Grayscale or false-color image representation
- Potential interference from environmental factors like ambient heat sources
Night Vision: Benefits and Disadvantages
The following are the advantages and downsides of night vision:
Benefits:
- High-resolution, natural-looking images
- Excellent visibility in low-light conditions
- Versatile applications in military, law enforcement, and outdoor activities
Disadvantages:
- Dependence on available light sources
- Limited ability to see through smoke, fog, or haze
- Generally more expensive than infrared technology
Color Night Vision vs. Infrared: Which is Better for Security Cameras?
When it comes to security camera applications, both color night vision and infrared technology have their advantages. Color night vision provides a more natural-looking image, making it easier for the human eye to identify and recognize people and objects. However, infrared technology is better suited for detecting heat signatures and can be more effective in complete darkness or poor visibility conditions.
For security purposes, the choice between color night vision and infrared often comes down to the specific needs of the application. Some best night vision security cameras now have both infrared and color night vision.
In scenarios where clear identification is crucial, such as in a retail environment, color night vision may be the better option. In contrast, for outdoor surveillance or applications where heat detection is more important, such as perimeter security, infrared technology may be the more suitable choice.
Best Security Camera with Night Vision Recommendation
Color Night Vision Security Camera - Reolink Argus 4 Pro
Reolink Argus 4 Pro is a 4K wireless color night vision security camera. Featuring Reolink ColorX technology, it uses an F/1.0 super aperture lens and a 1/1.8 sensor to capture four times more light, delivering vivid, true-to-life details even in low-light conditions. This camera ensures clear, colorful footage day and night.
4k 180° Wire-free Color Night Vision Camera
4K UHD 180° Blindspot-free View; Color Vision Day and Night; 30% More Battery Life; Dual-band Wi-Fi 6; Smart detection.
For users requiring full-color night vision without apparent spotlights, the Reolink Argus 4 Pro is the best option. Alternatively, if you desire an affordable choice that still delivers effective performance, the Argus 4 standard version is worth considering.
4k 180° Blindspot-free Wi-Fi 6 Camera
4K UHD 180° Blindspot-free View; Dual-band Wi-Fi 6; Smart detection; Easy Installation Anywhere
Security Camera with Color and Infrared Night Vision - Reolink Go PT Ultra
The Reolink Go PT Ultra is an excellent security camera that combines color night vision and infrared technology for enhanced visibility and performance. This 4K 8MP wireless camera is powered by a rechargeable battery or solar panel, making it a versatile and flexible option for a wide range of security applications.
The color night vision feature ensures that images captured in low-light conditions are crisp and clear, with natural-looking colors. This is especially useful for identifying individuals and objects. Additionally, the camera's infrared capabilities allow it to detect heat signatures and provide visibility in complete darkness, making it a valuable tool for security and surveillance.
4K 8MP Wire-Free 4G LTE PT Battery Camera
4K 8MP; Smart Detection; 355° Pan & 140° Tilt; Battery/Solar Powered; Color Night Vision; Smart Real-Time Alert.
FAQs
Which is better infrared or night vision?
The choice between infrared and night vision technology depends on the specific application and requirements. Infrared is better suited for detecting heat signatures and providing visibility in complete darkness, while night vision offers higher-quality, natural-looking images in low-light conditions.
Do all night vision cameras use infrared?
No, not all night vision cameras use infrared technology. While many night vision devices do incorporate infrared illumination to enhance visibility in low-light conditions, there are also night vision cameras that rely solely on amplifying available visible light to create the image.
Does the military use night vision or infrared?
Both night vision and infrared technology are widely used by the military for various applications. Night vision is commonly used for tasks such as covert operations, navigation, and target identification, where the ability to see clearly in low-light conditions is crucial. Infrared technology, on the other hand, is often employed for thermal imaging, target acquisition, and surveillance, where the detection of heat signatures is of importance.
Conclusion
The differences between night vision and infrared are significant and important to understand. While both technologies allow users to see in low-light or no-light conditions, they achieve this through fundamentally different working principles and provide distinct types of visual information.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with night vision and infrared technology in the comments below. Your insights and perspectives can help further the discussion and understanding of these fascinating visual technologies.
Search
Be in the Know
Security insights & offers right into your inbox



