RTSP vs RTMP: Which Protocol to Choose?

When it comes to streaming media, choosing the right protocol is crucial to ensuring a seamless and efficient experience. Two of the most popular protocols are Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) and Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP). While both serve the purpose of streaming media content, they each have distinct features and use cases.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between RTSP and RTMP and help you determine which best meets your specific streaming needs.
Basics of RTSP
First, let's look at RTSP, what it is, and how it works.
What is RTSP protocol?
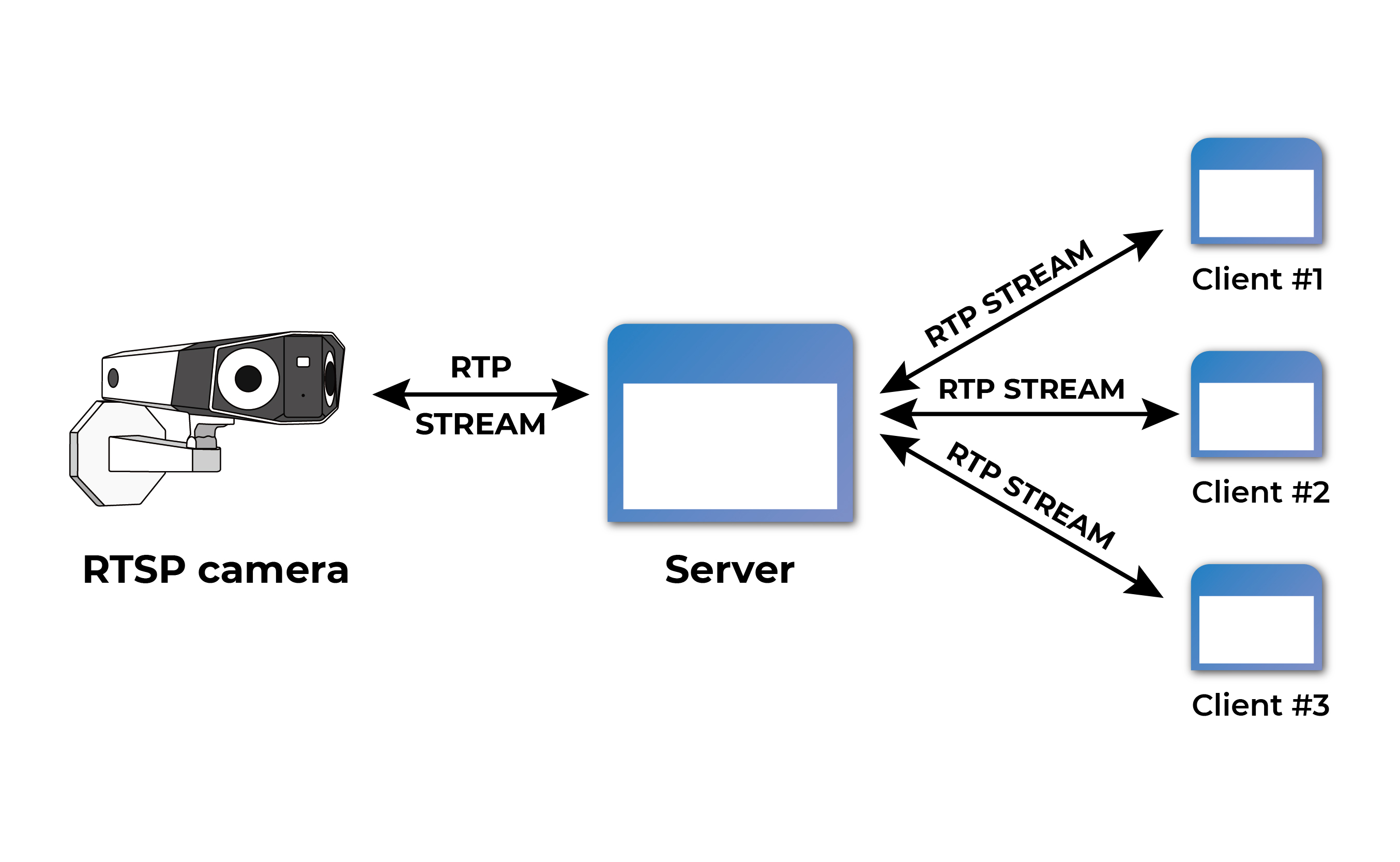
RTSP is short for Real-Time Streaming Protocol. It is a lesser-known protocol used for streaming video online. Its primary purpose is to control streaming servers in communication and entertainment systems. RTSP utilizes TCP for transmitting control commands and UDP for transferring video, audio, and other data formats. This combination allows users to play RTSP streams smoothly, even while downloading videos.
How does RTSP work for streaming?
When a user wants to transmit a video signal, their device sends an RTSP request to a dedicated server to determine available playback options. The server responds with supported requests. The user's device then receives a description of the video content from the streaming server and initiates the download.
RTSP relies on a dedicated server. It lacks support for retransmission of lost packets or encrypted video content. It is also incompatible with HTTP, which means that it prevents direct playback on web browsers. To enable playback on browsers, the original video stream needs to be converted, which it does by using an intermediate server.
Basics of RTMP
Now let's look at the same information about RTMP.
What is RTMP protocol?
RTMP stands for Real-Time Messaging Protocol. It is widely used for video-on-demand and real-time video streaming. It ensures a stable connection between the media server and Flash player by utilizing TCP for packet transfer.
RTMP has become the standard protocol for transmitting multimedia data over the internet. It offers low latency for on-demand and live video streaming, operating on top of TCP and sending data in smaller segments to maintain order. Despite the declining importance of Flash Player, RTMP is extensively used for streaming applications, with platforms like YouTube and Facebook relying on it for low latency streaming and connection stability.
How does RTMP work for streaming?
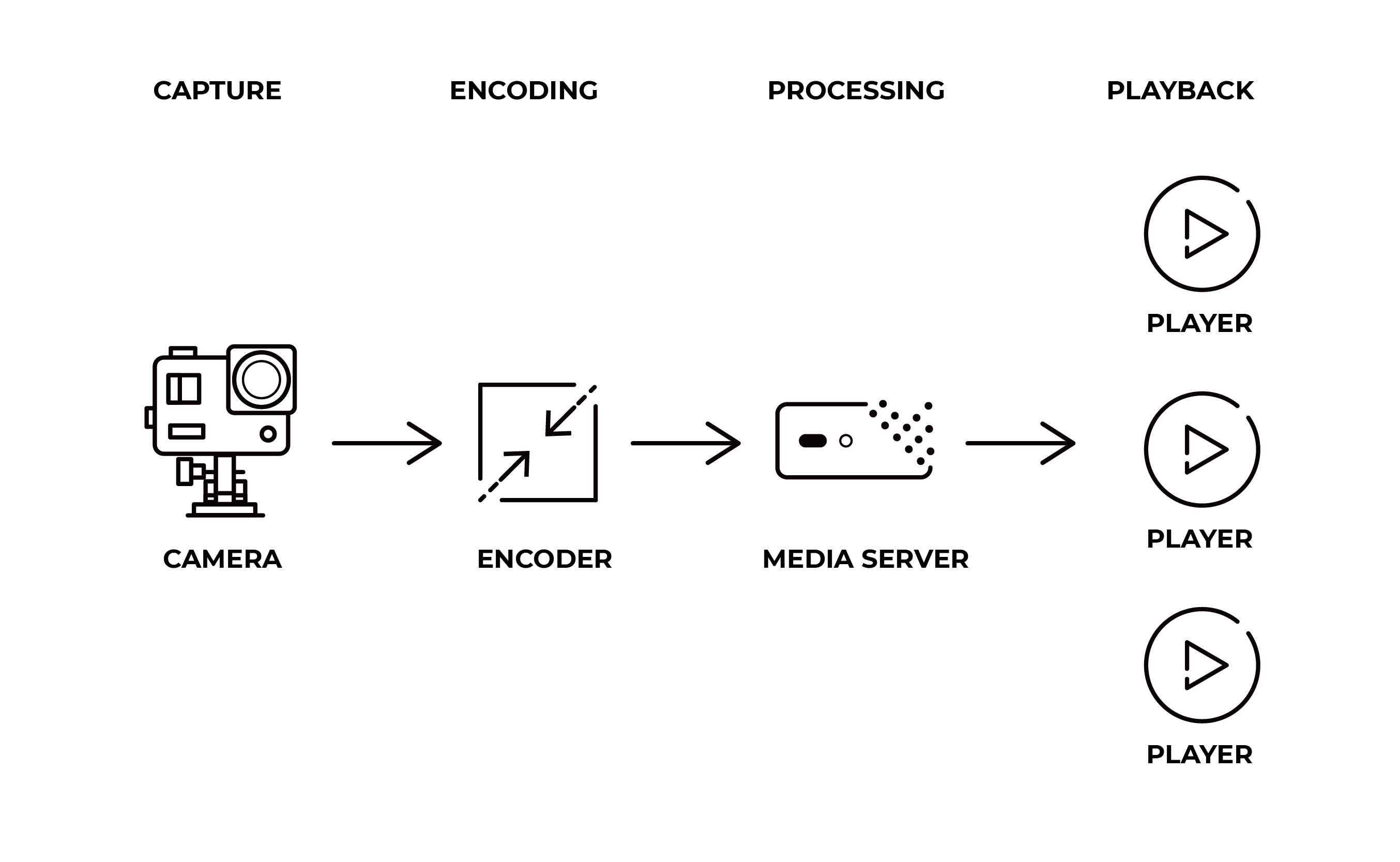
The RTMP streaming process consists of three main components: an encoder, a streaming server, and a media player. The encoder takes audio and video content and converts it into a streamable format, then sends the encoded data to the streaming server.
Acting as an intermediary, the streaming server distributes content to connected viewers. When a viewer wants to watch a live stream or video on demand, the media player sends a request to the streaming server. The server establishes a direct connection with the media player using the RTMP protocol and the encoded multimedia data is transmitted to the media player for decoding and playback.
RTSP Pros and Cons
Before selecting an RTSP live stream for your video delivery, it’s crucial that you know and understand all of the pros and cons.
RTSP Pros
-
Segmented Streaming: RTSP supports segmented streaming, allowing for efficient delivery of media content in smaller segments. Viewers have the advantage of being able to start watching the video without having to download the entire file beforehand.
-
Customization: RTSP offers flexibility and customization options, allowing users to control the delivery of multimedia content. It provides capabilities for controlling playback, recording, pausing, and rewinding, thus giving more control to content providers and viewers.
RTSP Cons
-
HTTP incompatibility: RTSP is not directly compatible with HTTP, which may limit its compatibility with certain devices and platforms. Users may need to use additional methods or technologies to integrate RTSP streams into web-based applications.
-
Less popular: Compared to other streaming protocols, RTSP is less widely known and used. This may result in fewer available resources, community support, and compatibility with various streaming servers and players.
RTMP Pros and Cons
Now let's examine the pros and cons of using the RTMP protocol for streaming media.
RTMP Pros
-
Low latency: RTMP minimizes the delay between content capture and viewer playback, making it ideal for live events where real-time interaction is crucial.
-
Adaptive bit rate streaming: RTMP allows broadcasters to deliver live streams in multiple quality levels, adapting to viewers' internet connections and device capabilities. This ensures a smooth viewing experience, regardless of varying network conditions.
-
Broad platform compatibility: RTMP is widely supported across platforms including desktops, mobile devices, smart TVs, and set-top boxes. This broad compatibility enables broadcasters to reach a larger audience on different devices and operating systems.
-
Interactive features: RTMP supports interactive elements like live chat, viewer polling, and simulcast. These features enhance viewer engagement and foster a sense of community during the live broadcast.
RTMP Cons
-
HTML5 incompatibility: RTMP relies on Flash players, which are becoming obsolete. RTMP streams cannot be played directly on HTML5 players without conversion tools like HLS, and requires additional steps for integration.
-
Bandwidth issues: RTMP streams can suffer from low video bandwidth, leading to frequent interruptions and a poor viewing experience for viewers.
-
HTTP incompatibility: RTMP cannot be streamed directly over HTTP connections. Special servers and third-party content delivery networks (CDNs) are needed to incorporate RTMP streams on websites.
RTSP vs RTMP: What's the Difference?
RTSP and RTMP share many similarities, but there are also some important differences. RTMP is particularly well suited to streaming high-quality content, whereas RTSP is better suited for low-latency streaming. Let’s look at the details.
RTSP vs RTMP: performance comparison
One significant difference between the two protocols lies in the level of control they each offer. RTSP provides greater control than RTMP, and as a result, RTMP is better suited for streaming live content. RTSP is more suitable for streaming pre-recorded media.
RTSP has lower latency compared to RTMP, which makes it faster. Latency refers to the delay between stream ingestion and the delivery of information to clients or end-user devices. Higher latency means more delay, which is not ideal for livestreaming. Unlike RTMP, RTSP does not require establishing a persistent connection, thus achieving lower latency. If you prioritize faster streaming, RTSP would be the better choice.
As for data transfer efficiency, RTMP outperforms RTSP every time. This is because RTMP can compress data during transmission, a capability that RTSP lacks. If your goal is to minimize data usage and transfer time, RTMP would be a better option.
RTSP vs RTMP: specification comparison
The following specifications comparison provides a technical overview of the differences between these two streaming protocols.
RTSP vs RTMP: Which Protocol is Best for You?
Now that you have a basic understanding the differences between RTSP and RTMP, you can make a better-informed decision on which protocol to use based on your specific application’s needs and requirements.
IP camera
Because IP cameras were in existence before the RTMP protocol was created, they widely support RTSP. RTSP’s simplicity and effectiveness in transmitting video signals means there is no need for modifications or changes when it’s used with IP cameras.
IoT devices
RTSP and RTMP both play crucial roles in streaming live video for a variety of IoT devices such as sensors, drones, robots, and cars. These devices not only transmit what they "see," but also enable real-time control. Many IoT devices are inherently equipped with native RTSP support in their software, ensuring seamless integration. Still, some manufacturers, including DJI, prefer RTMP for their devices.
YouTube, Twitch, Facebook
RTMP remains relevant as a receiving protocol in various third-party streaming services and applications, including YouTube Live, Twitch, and Facebook. This is the case despite the decline of Flash Media Player. Additionally, platforms like Zoom offer built-in support for outputting video streams via RTMP.
Additional Comparison: FLV vs SRT vs WebRTC vs ONVIF
This chart compares other streaming protocol differences:
FAQs
1. Is RTMP better than RTSP?
Choosing the best protocol between RTMP and RTSP depends on many factors, including desired latency, interactivity, control needs, and platform compatibility. To determine which protocol is best suited for your use case, evaluate each of these elements based on your specific streaming requirements.
2. Is RTSP outdated?
RTSP is not considered outdated, but it has seen decreased usage compared to other protocols. While RTSP remains a reliable and widely supported protocol for streaming media, newer protocols such as HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) and DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP) have been gaining popularity.
These protocols offer broader compatibility, adaptive streaming, and better integration with modern devices and platforms. However, RTSP still has its strengths, and continues to be used in various applications where its specific features and advantages are required.
3. Can RTSP and RTMP be used interchangeably?
RTSP and RTMP are not directly interchangeable due to differences in their protocols and intended use cases. RTSP is primarily focused on controlling the delivery of media streams, while RTMP is designed for real-time messaging and streaming of audio, video, and data. They have different underlying transport mechanisms, with RTSP using RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) for media transport and RTMP having its own proprietary protocol.
It is possible to convert streams from one protocol to the other using certain media servers or transcoding solutions. This conversion allows compatibility between RTSP and RTMP-based systems, enabling the streams to be used across different platforms or devices.
4. Do all IP cameras have RTSP?
While it’s not universal, the majority of IP cameras support RTSP. RTSP has become a common standard for streaming video from IP cameras due to its efficiency and compatibility with various media players and streaming servers.
Conclusion
Choosing between RTSP and RTMP requires careful consideration of your specific streaming objectives and requirements. While RTSP excels in control and delivery of real-time multimedia data, RTMP is preferred for low-latency communication and interactive applications. To make an informed decision, assess your performance, scalability, compatibility, and security aspects. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, so your choice should align with your specific streaming use case.
If you think this article could be helpful to someone you know, please forward it to them. If you have other questions about other protocols, leave a comment below!
Search
Be in the Know
Security insights & offers right into your inbox
