Solar vs Electricity: Which Energy Solution is Right for You?

When deciding between solar vs electric power, understanding their differences is key. Solar power converts sunlight into electricity through panels, while traditional electricity relies on grid-supplied energy from various sources.
In this article, we will compare both energy solutions. We will explore how each generates power and compare the costs and pros & cons. Whether for home energy or security systems, choosing the right option depends on efficiency, cost, and environmental impact.
Solar vs Electricity: Which One is Better?
The choice between solar vs electric involves balancing technical, financial, and practical factors that vary by location. Solar provides decentralized power generation through photovoltaic panels that convert sunlight to electricity right where it's used. It works by using silicon-based cells to create direct current from sunlight, which inverters then convert to usable alternating current.
Traditional electricity relies on centralized power plants sending energy through extensive transmission networks. It comes from a mix of sources including fossil fuels, nuclear and hydroelectric plants. This power travels through high-voltage transmission lines across long distances before reaching homes and businesses.
Pros and Cons of Solar Power
Pros of Solar Power
Energy Independence: Solar owners gain control over their energy supply and are protected against utility rate hikes. With battery storage, they maintain power during grid outages.
Financial Incentives: Beyond the 30% federal tax credit, many states offer additional rebates, property tax exemptions, and sales tax waivers.
Technology Advancements: New solar technologies promise higher efficiencies (potentially over 30%) and lower costs in coming years.
Cons of Solar Power
Intermittency Issues: Solar production varies seasonally, with winter output often 40-60% lower than summer peaks in northern climates.
Roof Requirements: Not all roofs are suitable. Ideal installations need south-facing surfaces with proper structural integrity and minimal shading.
Regulatory Barriers: Some homeowners associations and local governments impose restrictive regulations on solar installations.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Electricity
Pros of Traditional Electricity
-
Grid Stability: Large-scale power plants provide baseload generation that can instantly respond to demand fluctuations.
-
Universal Access: The existing grid infrastructure delivers power to virtually any location with minimal customer effort.
-
Load Flexibility: Consumers can instantly increase or decrease usage without capacity constraints.
Cons of Traditional Electricity
-
Vulnerability: The grid suffers about 3,500 significant outages annually in the U.S. due to weather, equipment failures, and cyber threats.
-
Environmental Costs: Electricity generation accounts for 25% of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions.
Price Uncertainty: Fuel costs and infrastructure investments lead to unpredictable rate increases over time.
Solar vs Electric Cost: Comparison Between Them
The financial analysis of solar vs electric cost requires examining both short-term cash flow and long-term value propositions. Solar represents a capital-intensive investment with delayed returns, while grid electricity operates on a pay-as-you-go model with ongoing expenses.
Solar Power Cost Details
A typical 8kW residential solar system costs $20,000−25,000 after federal tax credits, with prices varying by panel quality and installation complexity. Premium equipment commands a 10-15% price premium but offers higher efficiency and longer warranties.
The levelized cost of solar energy (accounting for the system's lifetime production) now ranges from 0.05−0.10 per kWh, which is cheaper than grid power in most markets. Solar panels typically degrade at 0.5% efficiency per year, still producing 85-90% of the original output after 25 years. Many utilities offer favorable net metering policies that effectively value solar exports at retail electricity rates.
Electric Cost Details
Residential electricity prices have increased at 2.5% annually over the past decade, with current averages ranging from 0.10/kWh (Washington) to 0.30/kWh (Hawaii). These rates include generation, transmission, and distribution costs, along with various regulatory fees and taxes.
Time-of-use rate plans charge higher prices during peak evening hours (often 0.25−0.40/kWh) when solar production declines. Customers in deregulated markets can choose competitive suppliers but remain vulnerable to wholesale price spikes, as seen during the 2021 Texas power crisis.
Solar vs Electricity: Which One to Choose?
The optimal choice between solar vs electric depends on a matrix of technical, financial, and personal factors that require careful analysis. Solar makes the most economic sense for homeowners with suitable roofs in states with high electricity rates (California, New York, Massachusetts) and strong solar incentives. The combination of energy savings, tax benefits, and increased home value typically delivers a 10-15% annual return on investment.
Traditional grid electricity remains the default choice for multi-family buildings, historic properties with roof restrictions, and areas with low electricity costs (under $0.12/kWh). Renters and frequent movers also benefit from the grid's flexibility without long-term commitments.
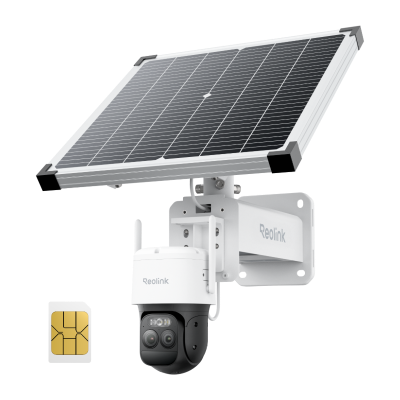
For security applications, solar-powered cameras provide superior reliability by eliminating dependence on grid power. Grid-powered systems work well for urban installations with reliable electricity but fail during blackouts without battery backups.
Bonus: Begin with a Solar-Powered Security System
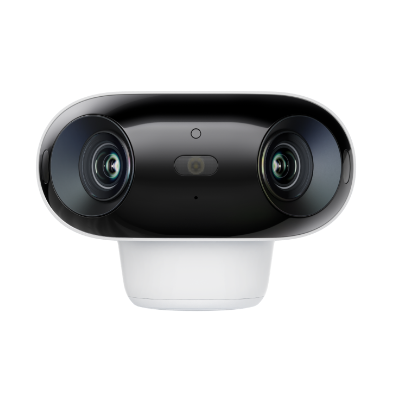
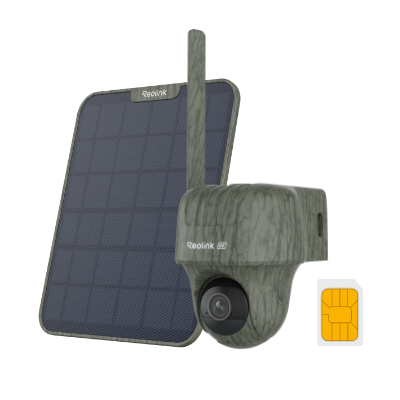
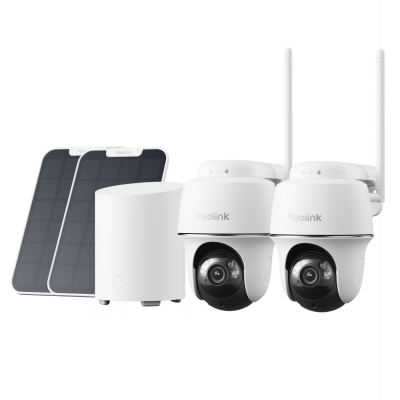
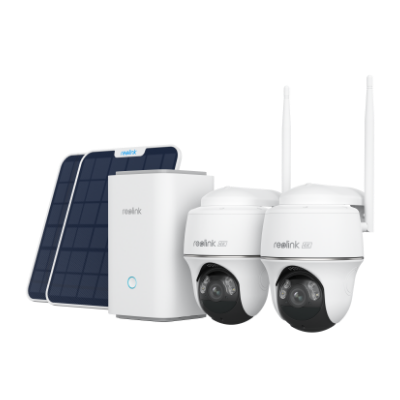
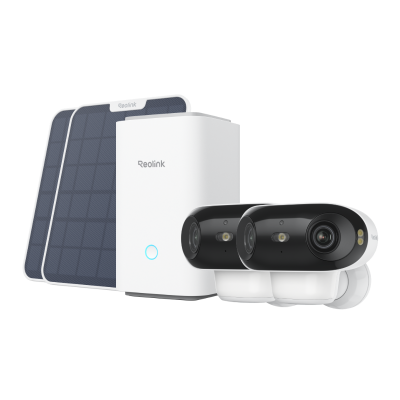
Home Hub with Argus 4 Pro
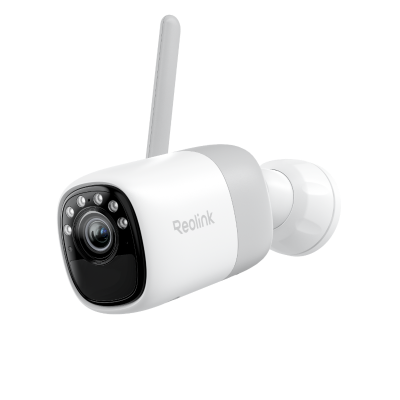
Argus 4 Pro is a solar-powered and wireless security camera system. It includes two Argus 4 Pro security cameras, two solar panels, and one Home Hub. The cameras contain a built-in battery that offers 30% more battery life and lasts for a long time. 10 minutes of charging is enough for 24 hours of performance.
They record videos in 4K resolution and cover a 180-degree field of view through two lenses. It's equipped with Reolink ColorX night vision to capture true colors even in extreme darkness. The Home Hub comes with a 64GB microSD card. It stores videos and sends real-time alerts without any monthly fee.
4K UHD Wi-Fi 6 Security System with 180° Blindspot-Free View
ColorX Night Vision, 1 Year of Local Storage, Exclusive Anti-Theft Algorithms, 180° Blindspot-Free Coverage, Expandable System Up to 8 Reolink Cams.
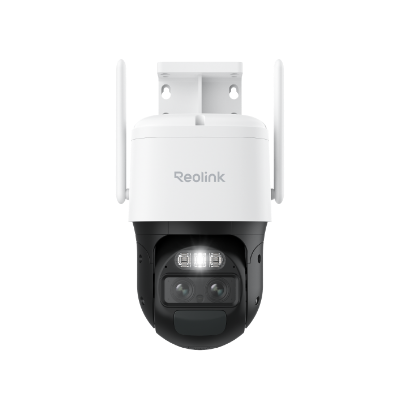
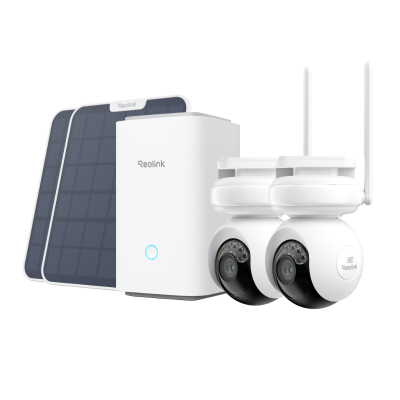
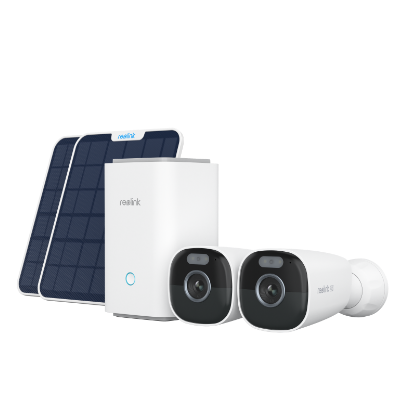
Home Hub with Argus Eco Ultra
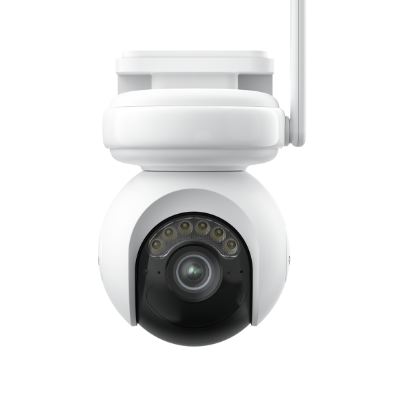
Home Hub with Argus Eco Ultra is a standalone solar-powered security camera system. It also includes two solar panels along with two security cameras and a Home Hub. The built-in battery is more than enough to offer reliable and non-stop performance.
The cameras record 4K colored footage all day. The colored night vision offers exceptional video quality at night. The Home Hub offers 1-year of local storage without any fee. It offers a regular security summary and works as a reliable alarm center.
Wireless Security System with 4K Wi-Fi Solar/Battery Standalone Camera Without Monthly Fees
4K Color Footage Day & Night, 1 Year of Local Storage, Exclusive Anti-Theft Algorithms, 360° All-Around Coverage, Expandable System Up to 8 Reolink Cams.
FAQs
Are solar panels cheaper than an electric bill?
After the payback period (typically 5-7 years), solar panels become significantly cheaper, saving homeowners $1,000−1,500 annually compared to grid electricity.
Is solar better than electric?
Solar is superior for environmental impact and long-term savings, while grid electricity offers greater reliability and convenience. The best choice depends on individual priorities.
How much can you save by going solar?
Most homeowners save $20,000−30,000 over 20 years, with system payback periods shortening as electricity prices rise.
Conclusion
The solar vs electric decision requires careful consideration of costs, reliability, and environmental impact. Solar power delivers long-term savings and sustainability but demands significant upfront investment. Traditional electricity offers convenience and reliability but lacks renewable benefits.
Search
Subscribe for the Latest Updates
Security insights & offers right into your inbox