AC vs. DC Power: What's the Difference? [2026]
The difference between AC vs DC power has played a defining role in the history of electricity. It's the discussion that has determined how we run our homes and power our devices and industries today. There exist distinct characteristics, advantages, and application scenarios for alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC).
We need to understand these differences to pick the right power supply for such requirements. So, this guide explains everything you need to know about AC vs DC electricity.
AC vs. DC Power: What They Are and Their Pros and Cons?
AC and DC power are the two main types of electrical current used today. While both deliver electricity, they work in fundamentally different ways and are suited to different applications.
What Is AC Power? Pros and Cons
AC power, or alternating current, is electricity that periodically changes direction. It is generated by power plants and delivered through electrical grids to homes and businesses worldwide. Because AC voltage can be easily stepped up or down using transformers, it is highly efficient for large-scale and long-distance transmission.
Pros:
- Efficient for long-distance power transmission
- Easy voltage conversion with transformers
- Standard for global power grids
Cons:
- Less efficient for energy storage
- Higher voltages can pose safety risks
What Is DC Power? Pros and Cons
DC power, or direct current, flows in a single, constant direction. It provides stable voltage, making it ideal for electronics, batteries, and renewable energy systems such as solar panels. Most portable devices rely on DC power, though conversion is often required to connect with AC-based systems.
Pros:
- Stable and consistent power output
- Ideal for electronics and energy storage
- Safer for low-voltage applications
Cons:
- Not suitable for long-distance transmission
- Requires conversion to interface with AC systems
DC vs. AC Power: What's the Difference?
By defining the advantages and limitations between DC vs AC power, we can see the most significant difference between DC (direct current) and AC (alternating current) power is that DC flows in a constant direction, while AC periodically reverses direction. Check out the details below:
Direction of flow
The most basic difference in AC vs DC current is how flow occurs. AC power changes its flow direction consistently, usually at a rate of 50 or 60 cycles per second, or 1 to 2 pulses each second. DC power flows in only one direction, one direction consistently.
Voltage levels and variation
Transformers can easily switch high and low voltage AC power levels, and transmit them long distances efficiently. DC power is different, as it often runs at a constant voltage for more efficient transmission, but less efficient for things like sensitive electronics.
Transmission efficiency and distance
Lower energy losses are a good reason for AC power to transmit electricity over long distances. DC power is, however, complex, and usually much better for short distances or localized systems like batteries and solar installations.
Safety
Since AC power uses oscillating voltages and has very high potential, it can be more hazardous. DC power is safer for low-voltage applications but presents a danger at high voltages from continuous electrical exposure.
Conversion
In converting AC to DC, one has simple rectifiers, but DC to AC is difficult and can even have the undesirable quality of adding unnecessary complexity and cost to certain systems with inverter components.
AC vs. DC Power: Comparison Table
AC Power vs. DC Power: Where to Use?
The ease with which AC and DC can be delivered versus received in specific applications determines which AC or DC power is used.
Where to use AC power?
AC power is the standard for residential and commercial power supply. It is used to provide power for home appliances, lighting, and HVAC systems. Industrial equipment including high-power machines use AC power.
Where to use DC power?
DC power is commonly used in portable electronics. It is used to safely operate smartphones, laptops, and wearables. Renewable energy systems also use DC power for energy storage solutions and solar panels.
Automotive systems have applications of DC power for hybrid powertrains, and electric vehicles. Lastly, low-voltage applications like LED lighting and sensors are a major use case for DC power.
AC or DC Power? Which to Choose?
The choice of AC or DC power depends on what you need. Consider the following:
- Find if the power is required for big transmissions (AC) or small applications (DC).
- Decide whether high voltage is needed for optimal performance or low voltage.
- Make sure that your new system fits in with the existing system or devices.
- Think of renewable energy systems that often use DC power.
- Look at the costs of conversion and setup through DC and AC.
AC or DC Power for Security Cameras?
DC power is a stable and common choice to power most plug-in security cameras. The reason why DC power is always a prime option for a security camera is the stability, ease of access, and portability. In most cases, these benefits come with wired, solar-powered, and battery-powered options.
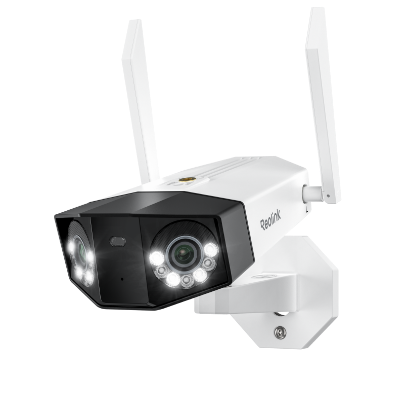
Powered by DC for stable operation, the Reolink Duo 3 Wi-Fi camera gives you dual lens coverage of a broader field of view. 16MP resolution, AI-powered detection, and color night vision make this camera perfect for home and business security.
Groundbreaking 16MP Dual-Lens WiFi Camera
16MP UHD, Dual-Lens, Motion Track, 180° Wide Viewing Angle, Plug-In WiFi, Color Night Vision.
FAQs
Is a house AC or DC power?
A typical house uses AC power. Homes receive alternating current from the electrical grid because it travels efficiently over long distances and works well with household wiring. Inside the home many devices actually convert this supply into DC power to run electronics like phones computers and LED lighting.
How to tell if power supply is AC or DC?
Check the label or rating plate first. Most adapters clearly state input and output type. AC usually lists voltage with a frequency value while DC shows a constant voltage symbol. Measuring with a multimeter also helps.
Is AC or DC power better?
Neither AC nor DC power is universally better. AC excels at delivering electricity over large areas and supporting everyday household needs. DC power is superior for electronics batteries and solar systems because it provides stable voltage.
Conclusion
In order to know how to make informed choices on energy systems, one has to understand the differences between AC vs DC power. AC power holds sway in large-scale transmission and in residential use across the world. Meanwhile, DC leads when it comes to localized, and portable applications. Both have good suits for unique needs. Choose between the DC vs AC power options and tell us what you think in the comments below!
Search
Subscribe for the Latest Updates
Security insights & offers right into your inbox

