Frequency Band: What is & How to Use

Frequency bands are the threads from which the new world communication is weaved. From ensuring a robust framework for wireless connectivity to being the foundational bricks of radar systems and broadcasting, different bands are hiding in plain sight.
It is important to understand the intricacies of frequency bands to improve their effective utilization. Don’t Worry! Today we will learn the basics of this term and common types. We also will explore their practical uses.
What is a Frequency Band?
Frequency bands are made from a set of frequencies that have clearly defined lower and upper limits. For communication, we use a range of frequencies within the electromagnetic spectrum to determine different types. The efficiency of the communication system and applications depends on the optimum utilization of these bands.
Types of Frequencies
Frequency wavelength bands can also be classified based on the range of frequencies they encompass.
L-band
Let’s start with understanding the L-band frequency. It can penetrate foliage and clouds effectively. This means there is no issue in transmitting a signal in cloudy weather. L band frequency covers frequencies ranging from 1 to 2 gigahertz (GHz).
Common Application:
- GPS (Global Positioning Systems)
- Satellite communication
- Aeronautical communication systems
S-band
On the second number, we have the S-band frequency range is from 2 to 4 GHz. S band frequency is best suited for long-range communications as it maintains a balance between antenna size and atmospheric absorption.
Common Application:
- Radio Astronomy
- Weather forecasting
- Radar systems
- Satellite communications
C-band
Consisting of frequencies from 4 to 8 GHz, C-band frequency is best known for providing reliable communication even for long distances. It can reduce signal attenuation caused by atmospheric conditions.
Common Application:
- Terrestrial microwave Communication
- Weather Radar systems
- Satellite communications
X-band
The X-band frequency had both military and civilian applications. It has shorter wavelengths. Hence, it is most reliable for accurate target detections and high-resolution imaging. Its frequency range spans from 8 to 12 GHz.
Common Application:
- Remote Sensing Application
- Radar systems
- Satellite communications
Ku-band
The most attractive feature of Ku-band frequency is the ability to transmit large amounts of data. This allows us to use Ku-band frequency for high-speed communication links. With 12-18 GHz, it features a higher frequency range.
Common Application:
- Direct Broadcast Satellite (DBS)
- Broadband internet services
- Satellite communications
Ka-band
Ka-band frequency ranges from 26.5 to 40 GHz. It is characterized by wide bandwidth. It is the main focus for 5G networks due to the ultra-high-speed transmission capability.
Common Application:
- Millimeter-wave radar systems
- Broadband internet services
- Satellite communications
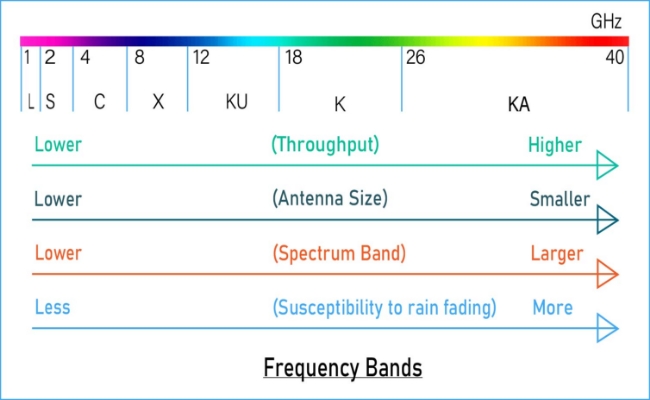
Frequency Band Charts
Frequency bands chart is the visual representation of electromagnetic frequencies. Each frequency is organized into unique bands with allocated applications and ranges. It showcases high frequencies such as terahertz spectrum (THF) and low frequencies (ELF).
The bands are standardized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The charts act as tools for reference for researchers and engineers in the telecommunications field. They provide valuable insights regarding different designated frequencies. For example, ELF is utilized for underwear communication. On the other hand, Terahertz Frequency is utilized for imaging.
Applications of Different Channel Frequency
Choosing the optimum hertz range is very important for operational efficiency. Now, let’s understand the industrial usage of various bands.
Wireless Communication
Once wireless communication appeared to be a miracle. Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and even cellular networks today have effective connectivity as they utilize the best-suited bandwidth.
Radio/Mobile Broadcasting
Today the audience can access vast content through radio and mobile with the help of the 5G network. Transmission of data signals and audio is managed using dedicated transmission bands.
Television Broadcasting
In television broadcasting, both audio and video signals are also transmitted by utilizing specific broadcast band. You can view the programs broadcast on television because the signals are transmitted over the airwaves.
Wireless LANs
The secure wireless LANs also utilize dedicated bands. A LAN network can be of various sizes. And different spectrums suit different networks.
Radar Systems
Radio bands are allocated to track and detect objects in a radar system. Some well-known examples are air traffic control radar, weather radar, and military surveillance radar. It helps in detecting objects both on the ground and in the atmosphere with accuracy and precision.
Bonus Tips: How to Check WiFi Frequency Band on Your Security Cameras
Many security cameras use WiFi to enable Internet connection. Some wireless security cameras can operate over dual-band WiFi. Here's how to check:
Use your other devices to detect the frequency bands. You can install a monitoring tool or software applications for the same. They will analyze the wireless signals to recognize the band. Check out the details of the manufacturer for insights into the supported bandwidth.

Dual-band Wi-Fi 6 Battery-powered Security Camera - Argus 4 Pro
Argus 4 Pro offers unmatched 4K Ultra HD resolution, capturing sharp and detailed video to ensure you don’t miss any important details. With advanced ColorX Technology, it provides stunning full-color night vision even in low-light conditions. The dual-band Wi-Fi 6 functionality ensures seamless 4K streaming with improved stability and reduced latency, making it easier to monitor your property in real-time without any interruptions.
4k 180° Wire-free Color Night Vision Camera
4K UHD 180° Blindspot-free View; Color Vision Day and Night; 30% More Battery Life; Dual-band Wi-Fi 6; Smart detection.
For consumers that require full-color night vision without apparent spotlights, the Reolink Argus 4 Pro is an excellent choice. Alternatively, if you want an inexpensive solution that still performs well, the Argus 4 standard version is worth considering.
4k 180° Blindspot-free Wi-Fi 6 Camera
4K UHD 180° Blindspot-free View; Dual-band Wi-Fi 6; Smart detection; Easy Installation Anywhere
FAQs
What are the 5 frequency bands?
Following are the 5 frequency bands:
- L-band frequency (1-2 GHz)
- S-band frequency (2-4 GHz)
- C-band frequency (4-8 GHz)
- X-band frequency (8-12 GHz)
- Ku-band frequency (12-18 GHz)
What are the frequency bands of 5G?
5G requires low latency and high speed, thus it utilizes multiple bands:
- Millimetre-wave
- Mid-band frequencies
- Low-band frequencies
Is a higher frequency band better?
Every coin has two sides. It depends on the use case. The advantage is higher data transmission speed and bandwidth. However, on the other side, the disadvantage is the shorter range and lack of ability for higher penetration.
Conclusion
Today’s communication is all about going wireless, thus frequency bands are essential for building the foundation of modern communication. The transmission systems operate smoothly and industries can incorporate accurate sensing because of electromagnetic bands. The knowledge of these bands is vital for professionals involved in telecommunications and related fields to ensure transmission efficiency and effectiveness.
Have you ever noticed the range of frequency bands of your devices? Do you think it is important? Share your thoughts with us! We'd love to hear from you!
Search
Subscribe for the Latest Updates
Security insights & offers right into your inbox


